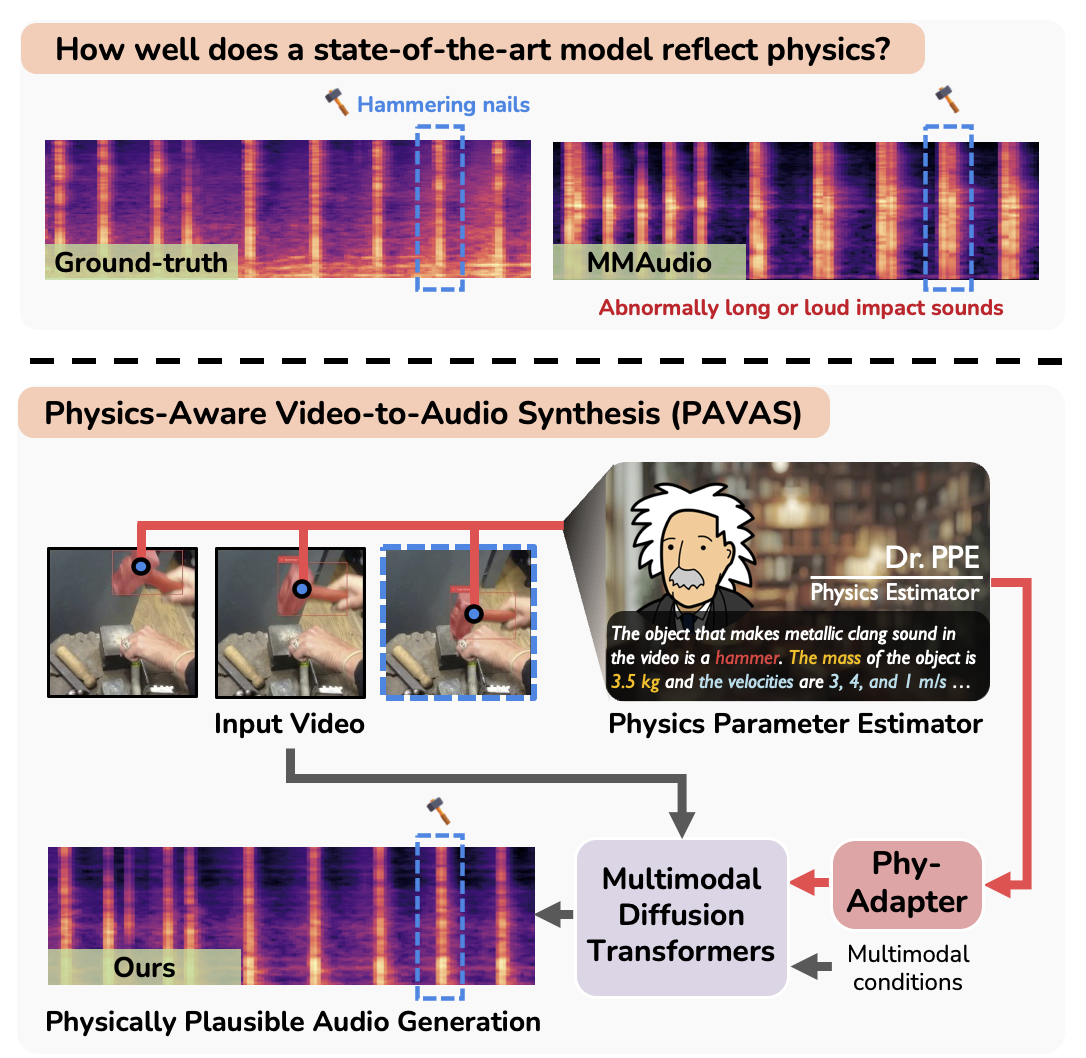
Recent advances in Video-to-Audio (V2A) generation have achieved impressive perceptual quality and temporal synchronization, yet most models remain appearance-driven, capturing visual-acoustic correlations without considering the physical factors that shape real-world sounds. We present Physics-Aware Video-to-Audio Synthesis (PAVAS), a method that incorporates physical reasoning into a latent diffusion-based V2A generation through the Physics-Driven Audio Adapter (Phy-Adapter). The adapter receives object-level physical parameters estimated by the Physical Parameter Estimator (PPE), which uses a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to infer the moving-object mass and a segmentation-based dynamic 3D reconstruction module to recover its motion trajectory for velocity computation. These physical cues enable the model to synthesize sounds that reflect underlying physical factors. To assess physical realism, we curate VGG-Impact, a benchmark focusing on object-object interactions, and introduce Audio-Physics Correlation Coefficient (APCC), an evaluation metric that measures consistency between physical and auditory attributes. Comprehensive experiments show that PAVAS produces physically plausible and perceptually coherent audio, outperforming existing V2A models in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
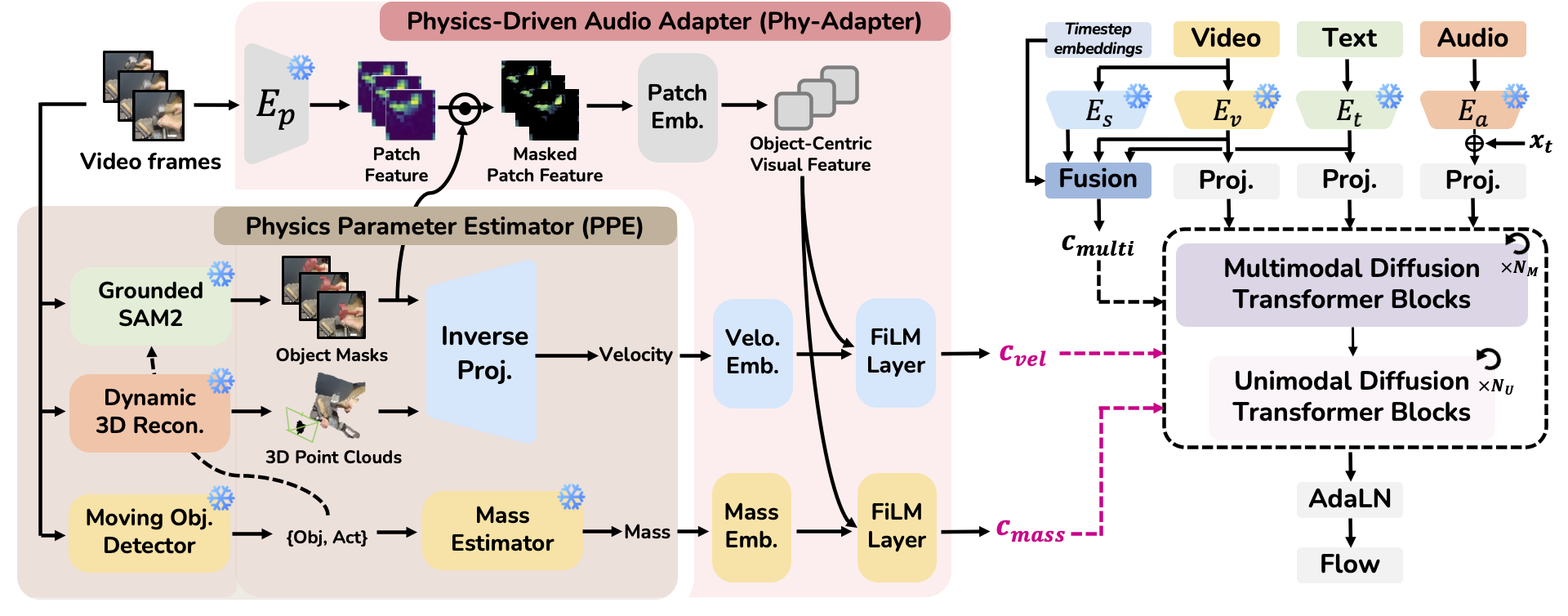
Given an input video, the Physics Parameter Estimator (PPE) extracts object-level mass and velocity. These physics cues are encoded by the Physics-Driven Audio Adapter (Phy-Adapter) and injected into the latent diffusion model alongside multimodal conditions.
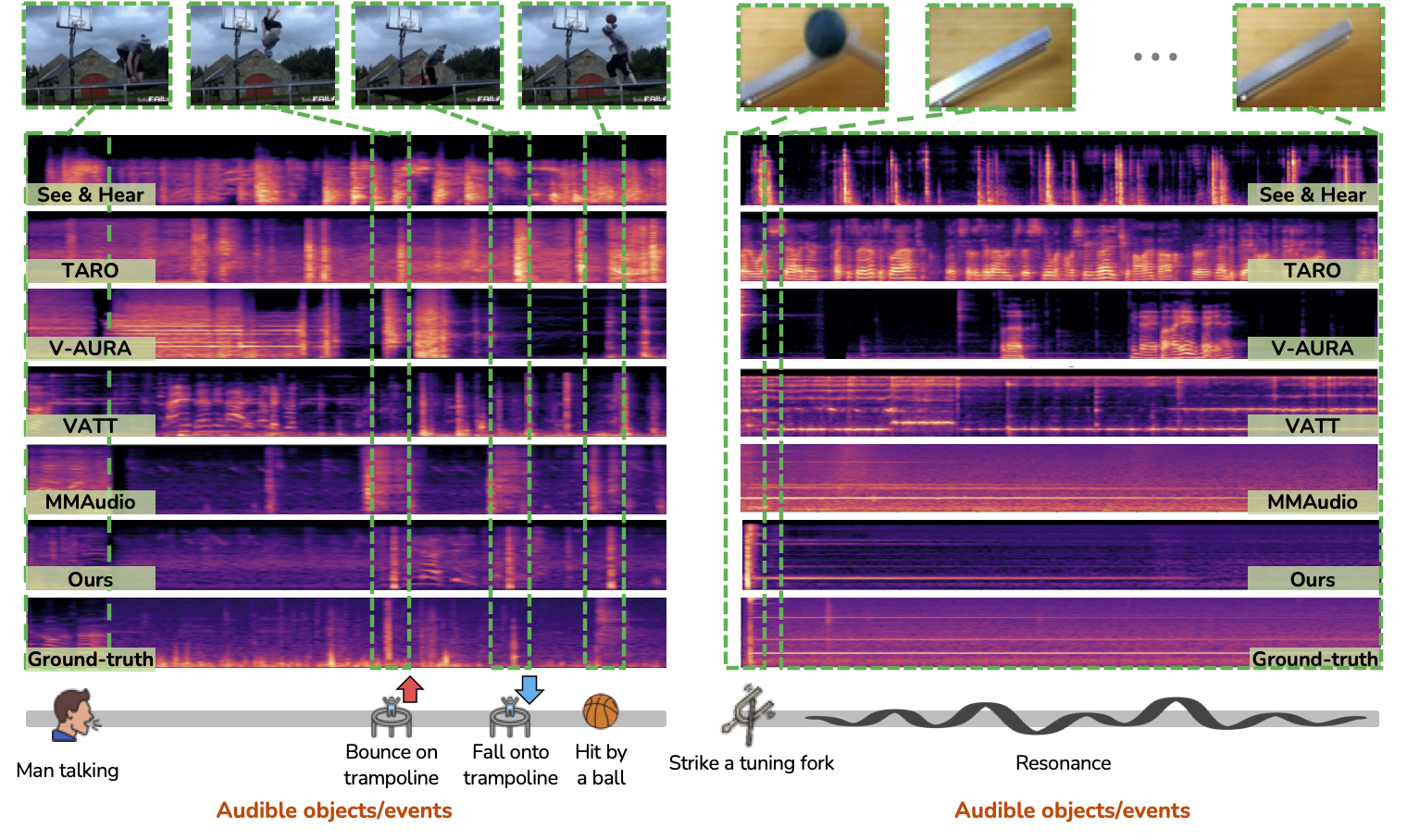
Samples 1&2
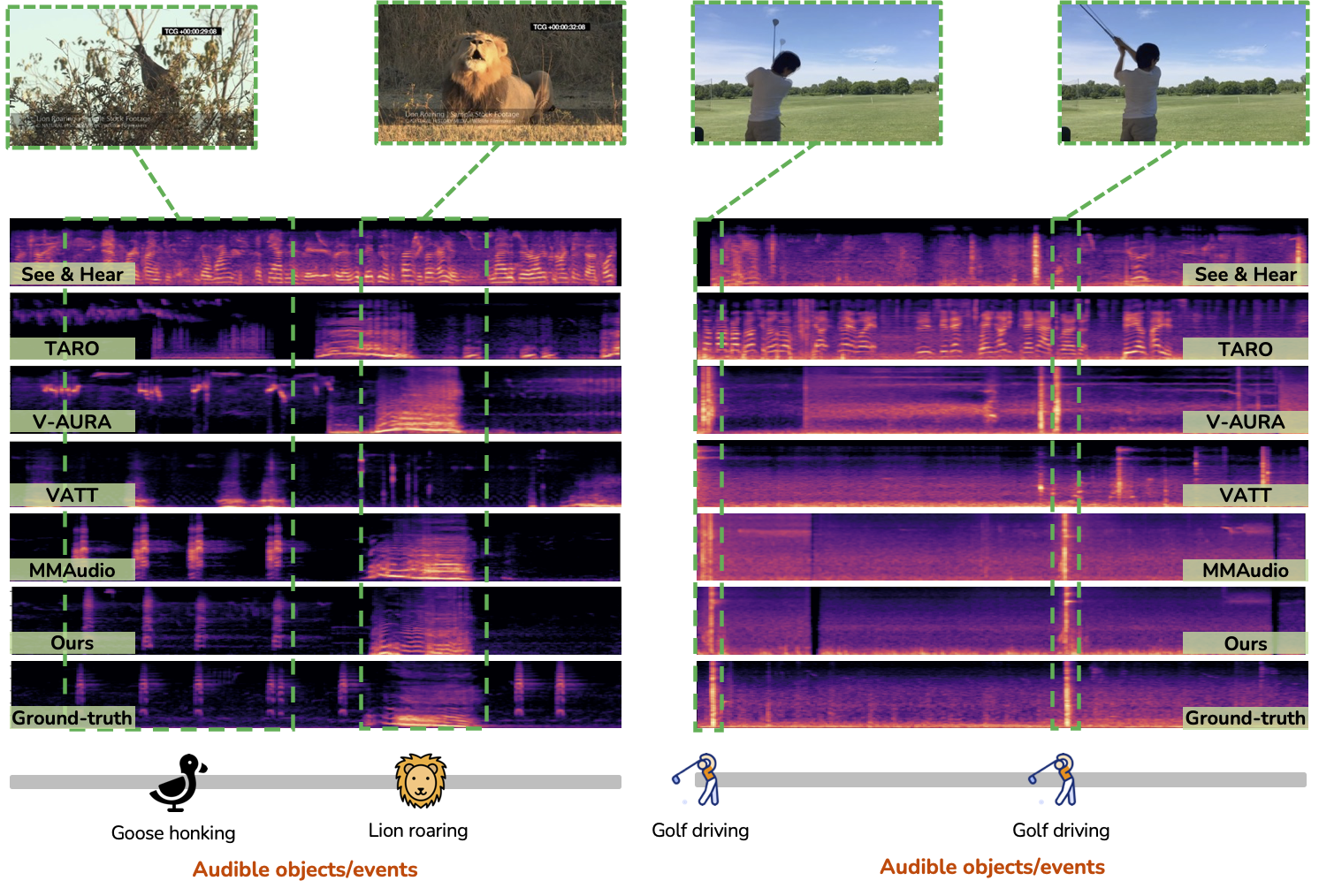
Samples 3&4
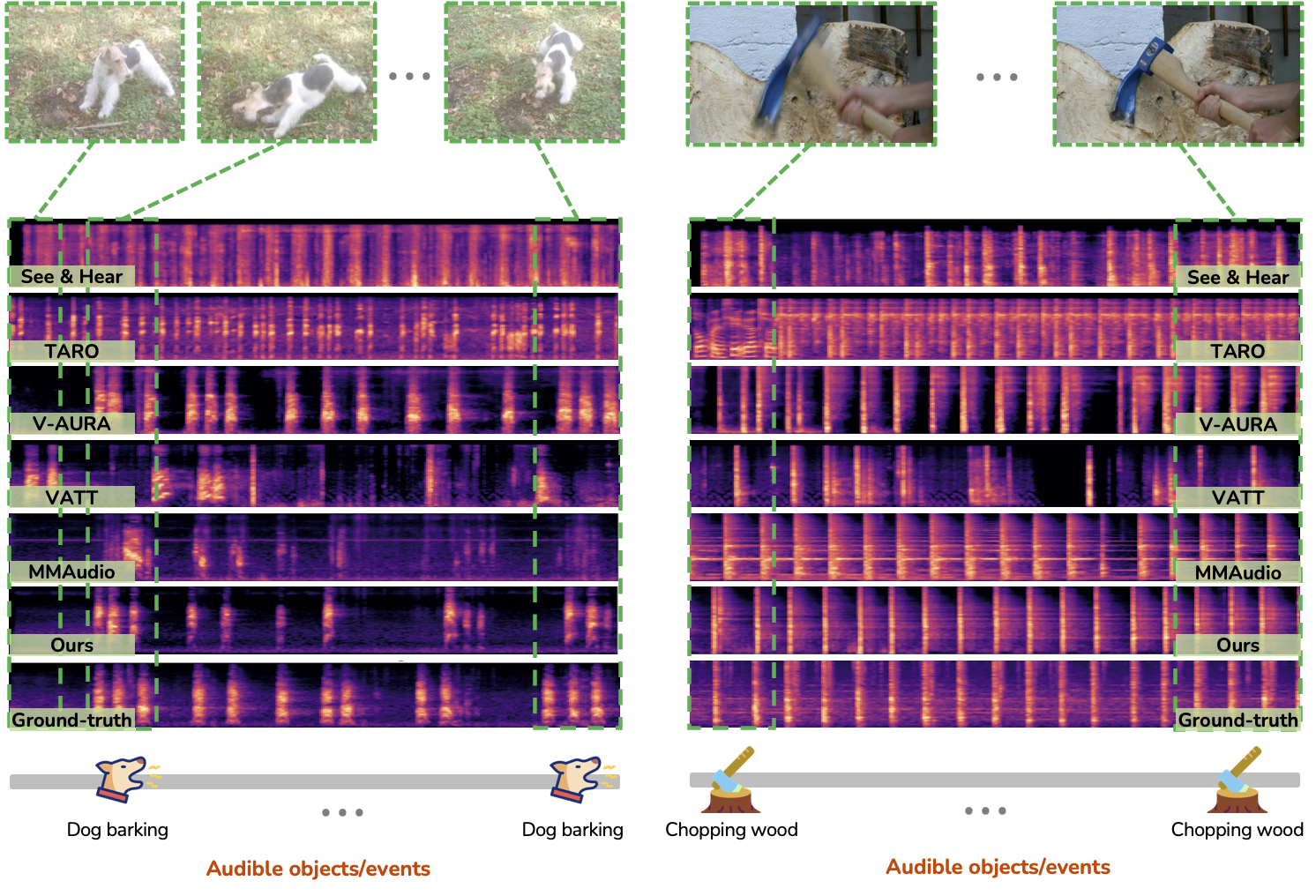
Samples 5&6
@article{hyun2025pavas,
title={PAVAS: Physics-Aware Video-to-Audio Synthesis},
author={Hyun-Bin, Oh and Takida, Yuhta and Uesaka, Toshimitsu and Oh, Tae-Hyun and Mitsufuji, Yuki},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.08282},
year={2025}
}